WiFi Mesh Network vs Range Extender - Which Is Better?
WiFi Range Extender or Mesh: For When A Router Isn't Enough
Most expect perfect WiFi coverage throughout with a single router. But, as you've probably noticed, that's usually not the case. Some rooms receive phenomenal WiFi, while in others, it’s difficult to stay connected.
Weak or spotty WiFi is often the result of building materials blocking WiFi signals and radio frequency interference.
Luckily, improving your WiFi coverage is made easy with a WiFi extender or mesh network.
Installers and Integrators
Take advantage of our system design and installation services. Learn more or call us for a free consultation: 1-800-969-8189
What is a WiFi Range Extender?

A WiFi range extender, as the name suggests, is a small device designed to extend the range of your WiFi signal. They are also known as WiFi boosters or repeaters.
The WiFi extender connects to your router wirelessly and repeats the WiFi signal via its own network. Thus, stretching your WiFi coverage and eliminating dead spots. Some extender models can be connected to the router using ethernet or a powerline connection.
Under optimal conditions, WiFi extenders can help achieve whole-home coverage for small homes or patch up small hard-to-reach areas in larger homes.
What is a WiFi Mesh Network?

A WiFi mesh network is a network made up of multiple WiFi nodes, also known as mesh extenders or satellites, that work together to blanket an entire home with reliable WiFi coverage.
Unlike WiFi range extenders, WiFi mesh systems replace your WiFi router. Though, they can be used with your existing router if needed as long as it's compatible.
Each node is linked to one another under a single network. You won’t have multiple WiFi networks covering your home. This solution is perfect for mid to large homes wanting whole-home coverage.
How Do WiFi Range Extenders Work?
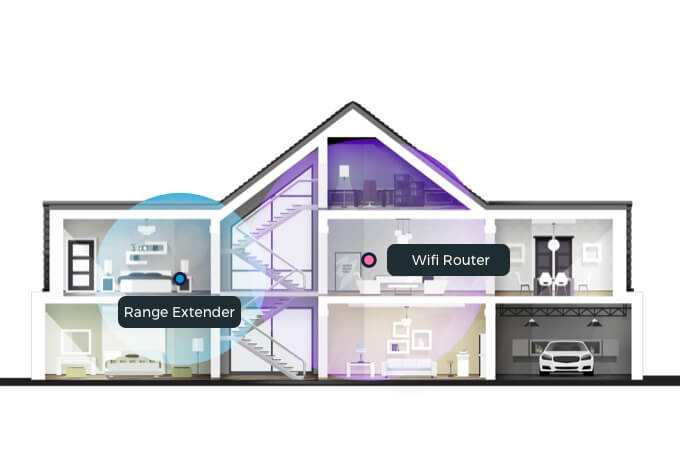
As you get further away from your WiFi router, the weaker the signal becomes. WiFi range extenders physically or wirelessly connect to your router. They take the WiFi signal and rebroadcast it into those hard-to-reach areas.
Ideally, the extender should be placed halfway between your router and the desired spot. However, if you decide to wire the extender, it could be placed anywhere since the signal is being transmitted through a cable rather than over the air.
Pairing your router and extender takes minutes. Different manufacturers (Tenda, InHand Networks, IP-COM, Netgear, TP-Link, etc.) have different setup and configuration processes. Consult your manual for installation instructions.
After the devices have been paired, the extender creates its own network for your WiFi-enabled devices to use. For example, if your home network’s SSID (name) is Nacho WiFi, the extender's name would be Nacho WiFi_EXT. While you’re roaming around your home, you’ll have to manually switch between networks. Automatic switching usually occurs when you're 100% out of range from one network and within range of the other. Some models boast "seamless switching" but it's always good to check your connection.
Range extenders vary in coverage, ranging from a few hundred to a couple of thousand square feet. Results depend on building layout and WiFi signal strength. Open-concept spaces will receive wider coverage than those with multiple walls. Similarly, extenders receiving a stronger WiFi signal can cover more than those placed in areas with weak signal.
In any case, you’ll be able to stay connected in areas where it was impossible to do so before.
How Do Mesh Networks Work?
WiFi mesh networks come with multiple mesh nodes. One node is required to be physically connected to your modem via ethernet, replacing your WiFi router. The other nodes should be placed within range of the mesh router or another node. Topology is extremely customizable.
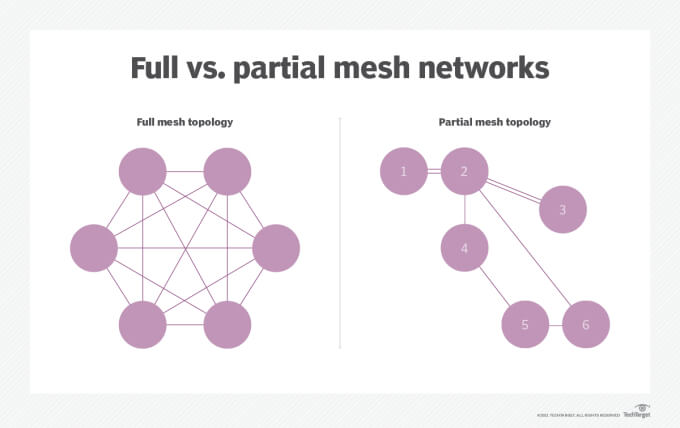
Image Source: TechTarget
Nodes can either communicate with each other via WiFi or wires. While a wired backhaul yields better results, a wireless backhaul is more common as not all homes are built with the needed wired infrastructure.
Every node operates under the same network. As you walk around your home, devices seamlessly connect to the closest node. You don’t have to switch networks like you would with a WiFi extender.

Designed with smart technology, mesh nodes work together rather than alone to blanket your home with reliable WiFi. All nodes are linked together and aware of each other. They’re able to identify the best path to the router even when a node is unavailable or busy, avoiding speed slowdowns.
The setup process is simple. Most mesh systems feature user-friendly apps. Through the app, you can access installation instructions, create guest networks, test connection quality between points, remove users from network, add parental controls, and more.
To learn more, visit What is a Mesh Network and How Does it Work.
Do WiFi Extenders Reduce Speed?
A WiFi extender doesn’t reduce the speeds provided by your internet service provider (ISP). However, range extenders tend to operate at reduced bandwidth.
A standard WiFi router only sends and receives data. A WiFi range extender does twice the work. It receives data from the router, rebroadcasts it, receives data from WiFi-enabled devices, and rebroadcasts it back to the router. Thus, capacity and speed generally decrease.
Some extenders are more prone to speed loss than others. For example, single-band extenders use a single WiFi frequency, either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz, to send and receive data. This can lower your bandwidth and internet speed by more than 50%.
Dual-band and tri-band range extenders with MIMO technology do a better job of mitigating speed issues. Dual-band units tend to dedicate a single band to sending or receiving data. The work is spread between two radios, increasing data transfer. With tri-band, two bands are dedicated to sending and receiving information while the third one is an exclusive link to the router. This ensures a faster and more stable connection.
Do Mesh Networks Reduce Speeds?
Since mesh networks use many nodes to send information, the data may have to do several wireless hops to reach the router. Every hop cuts speed just a little. Due to obstructions, distance, and signal repeating, speed will fluctuate throughout. AI is used to help lessen speed loss when transmitting data. Most people who have mesh networks experience steady signal speeds throughout their homes.
When transferring data, mesh WiFi systems use dual-band, tri-band, or quad-band technology. Like WiFi extenders, mesh networks use dedicated bands for nodes and connected devices.
Tri-band devices reduce congestion and improve WiFi speeds by using one 2.4 GHz band and two 5GHz bands. In other words, tri-band devices have double the bandwidth on the 5 GHz bands, which results in better speed and less congestion. Quad-band units add in the all-new 6 GHz band, further improving capacity and speed.
Do WiFi Extenders Really Work?
Yes.
As long as you have a good internet connection in your home and put the extender in the best location, they are sure to improve WiFi range.
Keep in mind that they probably won't stretch the signal throughout your entire home. Extenders are more like spot fixers, designed to improve dead zones in one or two areas.
Overall, wireless range extenders are an affordable and simple way of improving your WiFi network in small spaces.
TP-Link AC1200 WiFi Extender
- Dual Band, 5 GHz & 2.4 GHz
- Covers Up to 1,500 Sq Ft
- One Ethernet Port
- Supports Up to 30 Devices
- Simple Installation
The TP-Link AC1200 WiFi Extender is compatible with any WiFi router and offers up to 1,500 sq ft of coverage. It can connect up to 30 devices and provide dual-band speeds up to 1,200 Mbps. Once installed, your WiFi will reach places it couldn't before. This range extender is great for homes and offices.
Do Mesh Networks Really Work?
Yes.
Like extenders, if you have a reliable internet connection in your home and the nodes are strategically located, you will see immediate results.
Mesh networks are one of the most effective ways of improving your internet connection in large areas. Most kits come with 2–3 nodes. If that’s not enough, additional nodes can be integrated, making it easy to get whole-home coverage.
TP-Link Deco AX3000 WiFi 6 Mesh
- Dual WiFi 6
- Covers Up to 6,500 Sq Ft
- Three Ethernet Ports Per Node
- Supports 150 Devices
- Easy Installation, Seamless Roaming
With the TP-Link Deco AX3000 WiFi 6 Mesh, you can enjoy a stable internet signal throughout your home or office. It comes with three nodes, each with three ethernet ports for additional connection options. Together, they can cover up to 6,500 sq ft with dependable WiFi. Dual-band, it uses 2.4 and 5 GHz bands to transfer information. Super easy to set up, you’ll have whole-home coverage in minutes.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of WiFi Extenders?
Advantages
- Extends WiFi Coverage
- Helps Eliminate Dead Spots
- Easy to Install
- Cost Effective
- Compatible with Most WiFi Routers and Devices
- Compact and Discreet
- Easy to Move Around
- Ideal for Small Homes or Spot Coverage
Disadvantages
- Creates a Second WiFi Network
- Not Seamless, May Require You to Manually Switch Between Networks
- Can Reduce Speed
- Not Ideal for Whole-Home Coverage
- Placement is Vital
- Can be a Hassle Setting Up Multiple Range Extenders
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Mesh Networks?
Advantages
- Single Network
- Whole-home WiFi Coverage
- Use Multiple Radios to Mitigate Speed Loss
- Easy Setup and Configuration Process
- Eliminates Dead Spots
- Seamless Connection
- Use Smart Tech to Optimize Traffic Routing
- Self-Configuring
- Easy to Add and Remove Nodes
- Aesthetic Design
Disadvantages
- Pricier than Range Extenders
- While Simple, Set Up Can be Demanding
- Can be Overkill for Slow Internet Connections
- Each Node Requires More Power than an Average Range Extender
Can You Use a WiFi Extender with a Mesh Network?
All a WiFi extender needs to work is a power supply and WiFi. Thus, it can definitely be connected to a WiFi mesh network. However, it will not operate like a mesh node.
Devices may have difficulty switching between the mesh network and the extended network. This can lead to dropped connections and slower speeds.
If you can, it’s recommended to add a node rather than using a WiFi range extender.
WiFi Extender vs. Mesh: Quick Overview
The main differences between WiFi range extenders and WiFi mesh networks are:
Coverage
Extenders solve connectivity issues in smaller areas. Typically, they can increase WiFi coverage range by 300-2,000+ square feet. Mesh networking kits, however, provide whole-home coverage and are perfect for large homes. On average, they can cover areas from 2,000-5,500+ square feet. With additional mesh nodes, WiFi coverage can be extended even more.
Network Connection
Extenders create their own network with a separate SSID and password. Most of the time, users must manually switch back and forth between the main and extended networks. On the other hand, mesh nodes operate under a single network, establishing a seamless network. Devices automatically connect to the closest node.
Set-Up Process
WiFi extenders are simple to set up. When using multiple extenders, each device must be configured to work with your router. Depending on the manufacturer, installation may vary. To make the setup process as simple and fast as possible, mesh networks utilize user-friendly apps. On average, it takes less than 15 minutes to get the whole system up and running.
Flexibility
It’s possible to have more than one extender in your home or office. They must all be wired or wirelessly connected to your router, never to each other. Each extender will create its own network. To avoid network interference and confusion, each network must have a different SSID.
In contrast, mesh network apps make adding and removing nodes simple and fast. Adding a node further expands your WiFi coverage without adding additional networks to your home.
Price
There is a big difference in price between WiFi extenders and mesh systems. The best WiFi extenders will cost between $50-$80, while the best mesh systems range from $200-$500+. Additional nodes range from $100-$200.
So, Is Mesh WiFi Better Than WiFi Extenders?
Even though mesh networks and WiFi extenders both improve your wireless coverage, mesh networks are a lot smarter, work a lot better, and can expand your WiFi signal much further than extenders.
They are ideal for:
Gamers
One thing gamers hate is lagging in the middle of a kill shot. If lagging is not related to a slow internet service plan, mesh networks will improve your wireless connection. One could use an extender, but it may not be strong enough to fix lag issues.
Streaming Videos
If you love to stream movies at the best possible quality, you need a lot of bandwidth and speed. Most streaming companies recommend a consistent connection of at least 30 Mbps to stream a 4K video without a problem. Getting a stable connection from a router in a faraway room can be hard.
Extenders will keep you connected but may not be able to give you the bandwidth needed to stream without buffering. Since extenders share bandwidth with all connected devices, each device on the network could experience slower speeds which isn't ideal when streaming.
Even though mesh nodes also lose bandwidth after wirelessly connecting to the mesh router, they do a better job of managing incoming and outgoing data. With their advanced technology, you will always have a consistent signal in your room, allowing you to stream 4K movies without buffering.
Whole-Home Coverage
Large single-level and multi-level homes are more likely to experience dead zones in multiple areas. They tend to have more floors and walls blocking WiFi signals.
Many people would rather purchase WiFi extenders to patch up dead spots because they are more affordable. In many cases, to achieve whole-home coverage, multiple extenders are needed. This will result in multiple networks, which can be inconvenient.
Mesh networks, on the other hand, are seamless and hassle-free. You don’t have to worry about remembering to switch networks every time you move from the living room to your bedroom. Your wireless device will automatically connect to the closest node. Plus, the total cost of a mesh network might be cheaper than purchasing multiple extenders.
With that being said, if you can afford a mesh network, it would be ideal to invest in one.
Should I Get a WiFi Extender or Mesh Network?
Before you go and spend all your money, it’s best to check if you need an extender or mesh network by inspecting your current router and analyzing your network.
Router’s Location and Age
Sometimes signal issues are triggered by the location or age of your router.
Routers don’t always have the most aesthetically pleasing design, and when tangled cables are involved, they become an eyesore. For that reason, many people hide them behind furniture, in closets, or under desks, without realizing the negative effects this has on WiFi signals.
Materials like metal, concrete, plaster, windows, and wood are notorious for blocking and weakening wireless signals. We recommend moving your router to a central location to reduce the amount of WiFI blocking materials. This will improve the signal’s range and mitigate dead spots.
If moving your router did not work, or if moving the router is not practical, check if your router needs to be upgraded. Older routers are more susceptible to signal interference, slower speeds, and smaller coverage. New routers, especially those with the newest WiFi standards (WiFi 5 and WiFi 6), have better range capabilities and can support faster speeds.
Analyze WiFi Network Coverage
If your router is up to date and in the best possible location, we recommend analyzing your WiFi network coverage. Doing so will show you which areas have little to no signal. Based on the results you’ll be able to choose between a WiFi mesh network or WiFi extender.
The best and most accurate way of measuring your wireless signal strength is using decibel milliwatts (dBm) or testing your internet's download speeds, not by the WiFi logo on your phone.
Your network can be analyzed using free tools like InSSIDer Lite, WiFi Analyzer – WiFi Signal Meter App for Android, or WiFi Status App for Apple. With these tools, you should conduct various signal strength tests and speed tests in the locations where your WiFi connection matters.
WiFi signal strength test measuring:
- Less than –50 dBm is Excellent
- Between –50 and –60 dBm is Good
- Between –60 and –70 is Fair
- Greater than –70 dBm is Poor
Internet speeds, on the other hand, are measured in megabits per second (Mbps). They can range from 0 to the speeds your internet plan is capable of providing. For example, if your internet plan gives you up to 600 Mbps, your speed test will range from 0-600 Mbps. The higher the speed, the better.
Choose Between a WiFi Extender or Mesh Network
After analyzing your WiFi network, consider:
- How many weak to no signal areas there are
- The size of your home
- The number of floors your home has
If you found one or two areas with poor signal, and you live in a small home or apartment with three bedrooms or less, a range extender will be plenty.
On the other hand, if you live in a single-level home with more than three rooms, pay close attention to the location of the dead zones. Are they adjacent to each other or on opposite ends? Range extenders can help improve WiFi signals in neighboring rooms. However, it makes more sense to use a mesh network rather than multiple extenders when the dead spots are on opposite sides. This way you can have a steady connection throughout your entire home and don’t have to manually switch between different networks. In addition, there wouldn’t be a huge cost difference. A good extender will run you about $60, multiply that by two, and you’re looking at $120. Some 3-unit mesh networks cost as low as $150, only a $30 difference.
Multiple-level homes are more likely to have numerous areas with unreliable signal. They are larger and have more walls and floors interfering with WiFi signal. To improve your internet signal’s coverage evenly through multiple floors, a mesh network would be the best option.
Contact Us
Signal Boosters is a leading provider of cell phone signal boosters and WiFi solutions. We can help you eliminate cellular or Wi-Fi-related signal issues that fit your budget. Give us a call at 1-800-470-6777 with any questions you may have.
Interested in Learning More? Check Out Our Cellular Info Hub / WiFi Info Hub
Disclaimer: This blog contains affiliate links, which means that if you make a purchase through these links, we may earn a commission. However, this does not affect the integrity or quality of the recommendations provided.










